Personalized decision making powered by LLMs
Ability to reason is unexpected and hugely important skill to emerge out of large language models. Its effects on society and potential benefits are largely unexplored.
ChatGPT, and Large Language Models, the technology that powers ChatGPT, are on everyone’s mind. Journalists are using it to write news stories, and TV and movie story writers are taking a stand against it. It is even part of the geopolitical tension between China and the US.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are going to change the world but not just by writing news stories and TV scripts.
The ability to reason is an unexpected and important skill that emerged as LLMs developed and matured. People that regularly work with machine learning have noticed and understood its potential but its effects on society and potential benefits are largely unexplored.
For all the talk of personalization, technology is still cold and alien. People are expected to conform to apps and their devices. Automated reasoning at scale coupled with learning capabilities allow us to reimagine how technology is used by people.
The real change is going to be based on reasoning coupled with learning to create personalized agents. These agents will be able to make thousands of decisions in ways that align with owners' values. The agents will learn and evolve that decision-making process over decades based on their owner's experiences. They will even be able to learn the impact of decisions that were taken months, years, or even decades earlier. Humans call this learning from their mistakes. This has not been possible so far.
LLMs are going to get cheaper – by a lot
ChatGPT and LLM inferences (the answers generated by ChatGPT, and others are called inferences) are very expensive today. The cost of summarizing an average New York Times article is about 5 cents. This might not sound like a lot, but it prevents the personalization of LLMs at scale, leave alone personalized reasoning.
Reasoning based on LLMs is getting cheaper. By a lot.
The strongest argument for LLMs getting massively cheaper comes from a leaked document from Google. The document is worth reading in its entirety. We can learn a few things about the evolution of LLMs from this document.
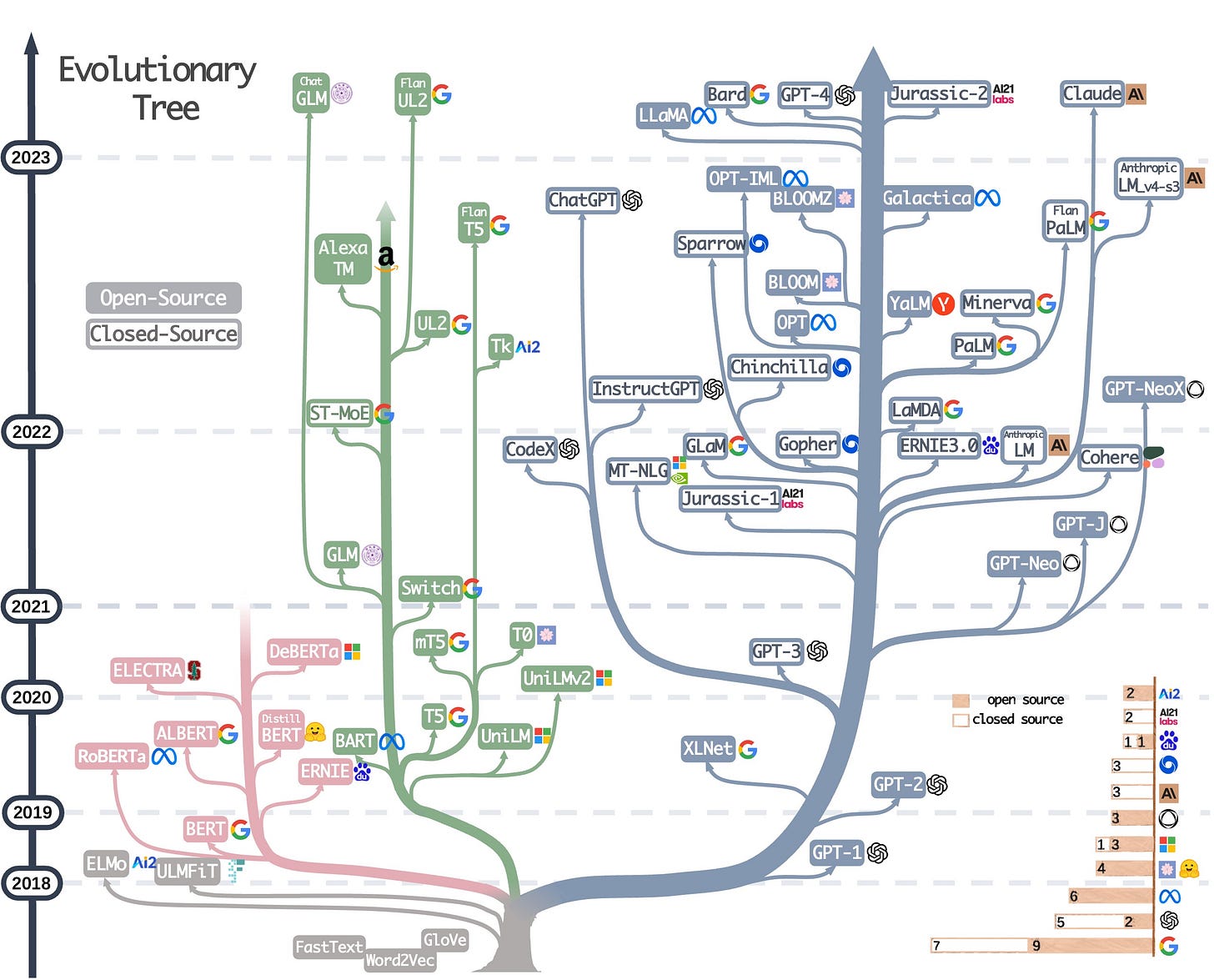
Open-source AI models are starting to catch up with commercial models like those from OpenAI, Cohere, and Anthropic. See the image below for how open-source LLMs have proliferated in the last two months. Two months!
Fine-tuning large language models is getting very inexpensive. A technique called Low-Rank Adaptations (LoRA) allows someone to fine-tune for about $100. Even this might be considered for many use cases.
Fine-tuning with in-context learning allows the deployment of customized LLMs.
We can now talk about deploying a LLM customized for each person, based on their own life that is fine-tuned to their values and how they would make decisions.
This means that anyone can start with a reasonably capable model, retrain it for their use case, and use it with effectively zero effective costs.
Personalized decision-making powered by LLMs
As we move into the era of LLMs and personalized reasoning engines, we will witness a transformation in how individuals make decisions. The concept of reverse personalization, which focuses on assisting individuals in making decisions based on their unique values and experiences, will serve as a driving force for this change. As LLMs become more affordable and widely accessible, AI-based agents and reasoning engines will be increasingly integrated into our daily lives.
Imagine a world where every individual has access to their personalized AI assistant, helping them make informed decisions, from choosing the best educational path to maintaining healthy relationships. Reverse personalization will empower individuals by ensuring that their decisions are based on their values and experiences, leading to a more fulfilling and authentic life.
Changes to our society are going to be driven not just by AI but a marriage of convenience between AI and Robotics. At De-Magic we use a quantitive and open-source model called the Jobs Impact Quotient to evaluate about how AI and Robotics will impact jobs.
You can read more about the differences between algorithms and machine learning models or how to monetize open-source projects.

